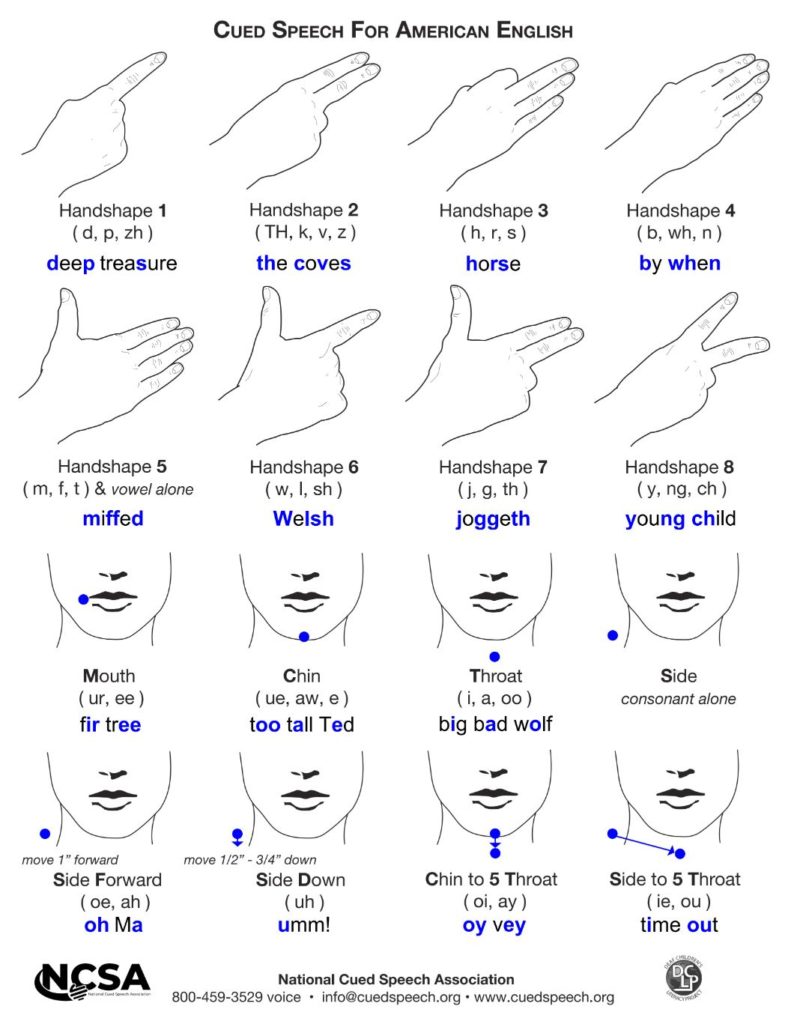
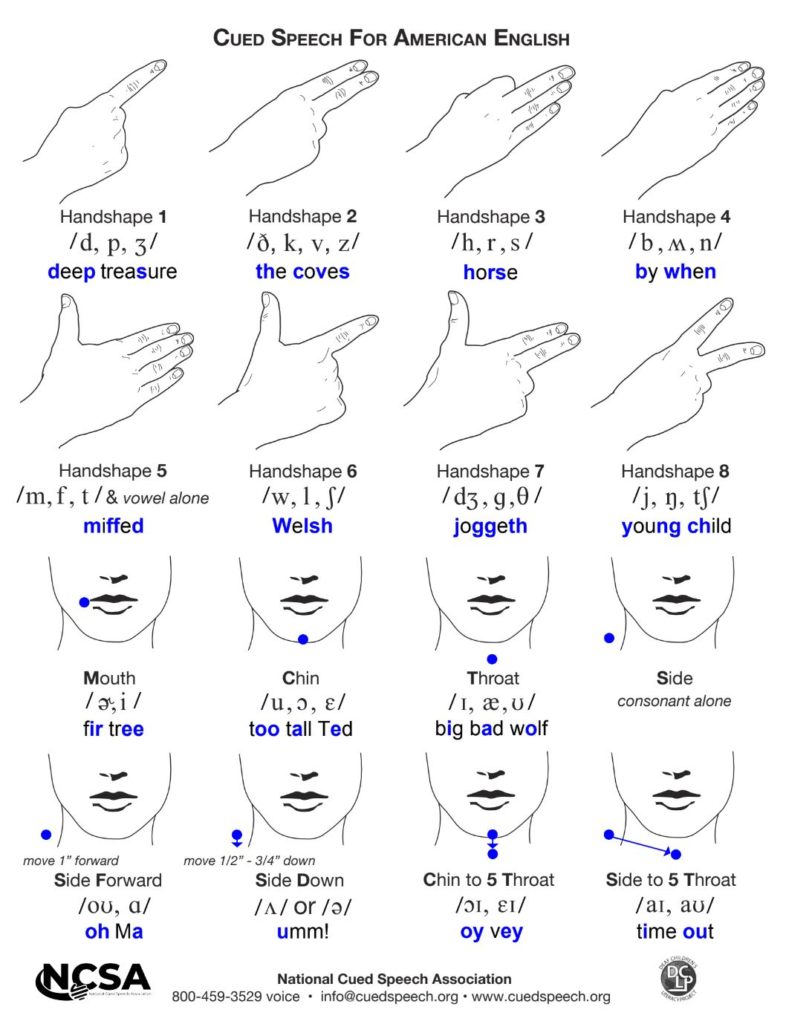
The entire Cued Speech system is typically taught in 8-12 hours of classroom time. For many, Cued Speech is easy to learn! Beginners can start with the Cued American English charts [Standard|IPA] and Cue College’s self-paced, online introductory CS100 course.

Anyone who is a family member of a child with hearing loss or another communication challenge can learn the entire Cued Speech system for American English for free by signing up for the Cue College “Cue Family” program. Learn at your own pace using our self-study online course, “CS100 – Introduction to Cued American English” and get a FREE one-year membership to the NCSA. For more information and/or to register for our free Cue Family program, please visit the Cue Family Program site.
Anyone else who wants to learn to cue can visit Cue College and choose to learn via the Cue College CS100 self-study course, our CS101 instructor-led course, and/or our interactive one-on-one Cue Tutor program.
Cued Speech classes are also available via in-person and virtual workshops and camps. Check our Find an Event page for upcoming offerings.
Educational Video Series
The National Cued Speech Association provides educational videos for interested parents, language professionals and the general public to learn more about cued language.
How Cued Speech Supports Language and Literacy Development – Presented by the National Cued Speech Association. This webinar features important information for parents of deaf or hard of hearing children as they navigate language development. Over 90% of deaf children are born to hearing parents. A child’s first and primary language model comes from his or her parent(s). Vocabulary, range/depth of word knowledge, comprehension, word recognition, and English phonology are critical to development of a child’s language skills.
